What is Resin Epoxy?
- Resin Epoxy is a two-part synthetic polymer material that, when mixed together, undergoes a chemical reaction resulting in a durable, high-strength, and adhesive substance. Resin epoxy is a versatile, high-performance material used for various industries, including construction, automotive, electronics, artistic, and DIY applications. It is composed of two main components, a resin and hardener. When these components are mixed, chemical reaction occurs, causing the liquid mixed with resin and hardener to turn into a solid form, durable plastic like material. This curing process can vary in time Depending on the Specific formulation of the epoxy, ranging from a few hours to several hours.
- Epoxy resins are known for their strong adhesive properties, chemical resistance and excellent mechanical strength. These characteristics make them ideal aur bonding different materials such as wood, metal, glass and plastics. In addition, epoxy is often used as a protective coating because of its ability to resist water, chemicals, and UV light, which helps protect surfaces from corrosion and wear.

Why is Resin Epoxy Popular?
- Resin has gained widespread popularity due to its remarkable versatility, durability and aesthetic appeal across various industries. One of the key reasons for its popularity is its adaptability in both Industrial and creative applications. Resin, particularly epoxy resin, can bond with a wide range of materials, including wood, metal glass and plastic, making it a go to solution for construction, repair and manufacturing process. Its strong adhesive properties, coupled with resistance to chemicals, moisture, and heat, ensure long-lasting results in demanding environments.
- In the arts and craft sector, resin is cherished for its ability to create visually stunning pieces. Its glossy clear, glass like finish can be easily tinted with pigment, offering endless possibilities for customisation.
- Additionally, resins popularity is driven by its role in protective coatings. Its capacity to form a hard, durable surface makes it ideal for flooring, counter tops, and other services exposed to heavy wear and tear. In the automotive and marine industries, resin is used for its waterproofing and corrosion resistant property, ensuring that vehicles and structures remain protected over time.

History and Development
- The history and development of the epoxy region track back to the early 20th century when chemists were exploring synthetic materials that could replicate or improve upon the properties of natural substances. The development of the epoxy resin began in 1936 Dr. Pierre Castan, a Swiss chemist, and Dr. S.O. Greenlee the United States Independently developed epoxy compounds. Castan worked on synthesizing epoxides for dental materials, while Greenlee was focused on creating a new type of resin. Their combined imports LED the groundwork for the epoxy resins we know today.
- The breakthrough came with the development of the bisphenol-a-based-epoxy resin, which is still one of the most commonly used forms. This type of epoxy resin was first commercially produced by the chemical company Ciba in the late 1940s. The material quickly gained popularity due to its strong adhesive properties, excellent chemical resistance, and ability to bond with a wide range of materials, epoxy resin early applications were primary in coatings, and adhesives, particularly in industries that required materials capable of withstanding the environment, such as the aerospace and marine sectors.
Types of Resin Epoxy
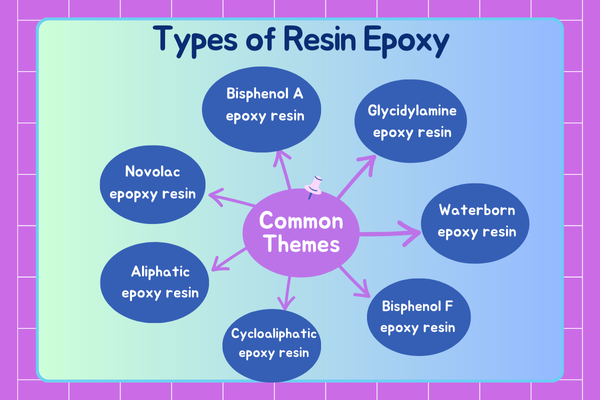
Epoxy resins are widely recognized for their versatility, strength, and durability. Used across various industries such as construction, automotive, aerospace, electronics, and even art, epoxy resins come in different types, each tailored to specific applications and requirements. Understanding the types of epoxy resins can help in selecting the right material for your project. Below, we explore the main types of epoxy resins, their properties, and typical uses.
1. Bisphenol A Epoxy Resin
Bisphenol A (BPA) epoxy resin is one of the most common types of epoxy resin. It is synthesized by reacting bisphenol A with epichlorohydrin. BPA epoxy resins are known for their excellent mechanical properties, strong adhesion, and resistance to chemicals.
Properties:
- High mechanical strength
- Strong adhesive properties
- Good chemical and moisture resistance
- Moderate viscosity
Applications:
- Coatings: Used extensively in protective coatings for metals and concrete, particularly in industrial settings where resistance to corrosion and chemicals is required.
- Adhesives: BPA resins are favored for their bonding strength, making them ideal for construction and automotive adhesives.
- Electronics: They are used to encapsulate and insulate electronic components due to their good electrical insulation properties.
2. Bisphenol F Epoxy Resin
Bisphenol F (BPF) epoxy resin is similar to BPA epoxy but is synthesized using bisphenol F instead of bisphenol A. This variation results in a lower viscosity and improved chemical resistance, making it suitable for different applications.
Properties:
- Lower viscosity compared to BPA resins
- Enhanced chemical resistance
- Good flexibility
Applications:
- Composites: BPF resins are often used in composite materials, such as fiberglass, for applications that require a balance of strength and flexibility, like wind turbine blades and boats.
- Coatings: Used in high-performance coatings that need to withstand harsh chemicals and environmental conditions.
- Adhesives: Employed in adhesives where a strong, flexible bond is needed, particularly in industrial settings
3. Novolac Epoxy Resin
Novolac epoxy resins are derived from phenolic resins and offer higher cross-link density compared to BPA and BPF resins. This results in superior thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength, making them suitable for demanding applications.
Properties:
- High thermal stability
- Exceptional chemical resistance
- Increased mechanical strength
Applications:
- High-Temperature Coatings: Used in environments where high heat and chemical exposure are common, such as in oil and gas industries.
- Structural Adhesives: Employed in aerospace and automotive industries where materials must withstand extreme conditions.
- Composites: Novolac resins are used in high-performance composites for applications requiring enhanced durability and resistance to harsh environments.
4. Aliphatic Epoxy Resin
Aliphatic epoxy resins are made from non-aromatic hydrocarbons, making them distinct from the aromatic-based BPA and BPF resins. These resins are prized for their excellent UV resistance and outdoor durability.
Properties:
- Outstanding UV resistance
- Good clarity and color stability
- Lower mechanical strength compared to aromatic resins
Applications:
- Outdoor Coatings: Used in coatings that must maintain their appearance and performance when exposed to sunlight, such as in exterior paints and vehicle coatings.
- Clear Coatings: Ideal for decorative applications due to their clarity and resistance to yellowing under UV light.
- Outdoor Adhesives: Aliphatic epoxies are used in adhesives for structures exposed to the elements.
5. Glycidylamine Epoxy Resin
Glycidylamine epoxy resins are based on glycidylamines rather than bisphenols. They offer superior thermal and chemical resistance, making them suitable for high-performance applications where strength and durability are critical.
Properties:
- Superior thermal stability
- Exceptional chemical resistance
- High mechanical strength
Applications:
- Aerospace Composites: Used in the production of lightweight, high-strength composites for aerospace applications.
- High-Performance Adhesives: Employed in applications requiring adhesives that can perform under extreme conditions, such as in automotive and aerospace sectors.
- Thermal Management Materials: Glycidylamine resins are used in materials that manage heat in electronic devices.
6. Cycloaliphatic Epoxy Resin
Cycloaliphatic epoxy resins are a specialized type of aliphatic epoxy resin, featuring a cycloaliphatic structure that provides excellent electrical insulation and UV resistance.
Properties:
- Excellent electrical insulation properties
- Good UV resistance
- Low viscosity
Applications:
- Electrical Insulation: Used in producing insulating materials for electrical components like transformers and insulators.
- Outdoor Coatings: Their UV resistance makes them suitable for coatings exposed to sunlight and harsh weather conditions.
- High-Temperature Adhesives: Cycloaliphatic resins are used in adhesives that require both thermal stability and electrical insulation.
7. Waterborne Epoxy Resin
Waterborne epoxy resins are emulsions or dispersions of epoxy resin in water. These resins are developed to reduce environmental impact by eliminating harmful solvents and reducing volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
Properties:
- Low VOC emissions
- Good mechanical properties
- Reduced environmental impact
Applications:
- Environmentally Friendly Coatings: Used in architectural and industrial coatings where environmental regulations require low VOC emissions.
- Adhesives: Employed in applications where solvent use is restricted, such as in eco-friendly construction.
- Sealants: Used as sealants for concrete, wood, and other materials without the harmful emissions associated with solvent-based systems.
8. High-Temperature Epoxy Resin
High-temperature epoxy resins are specifically formulated to withstand extreme temperatures, often up to 250°C or higher. These resins are designed for applications where conventional epoxy resins would fail due to heat degradation.
Properties:
- Exceptional thermal stability
- High mechanical strength at elevated temperatures
- Good chemical resistance
Applications:
- Aerospace and Automotive: Used in components that are exposed to high temperatures, such as engine parts and exhaust systems.
- Industrial Applications: Employed in environments where high heat resistance is crucial, such as in foundries and manufacturing plants.
- Electronics: Used in thermal management systems for electronic devices that generate significant heat.
9. Flexible Epoxy Resin
Flexible epoxy resins are designed to provide flexibility and toughness, unlike traditional epoxy resins, which are often rigid and brittle. These resins maintain strong adhesive properties while allowing for movement and deformation.
Properties:
- Enhanced flexibility and toughness
- Strong adhesive properties
- Good impact resistance
Applications:
- Flexible Adhesives: Used in applications where materials need to expand, contract, or absorb impact, such as in construction joints and automotive parts.
- Coatings: Flexible epoxy coatings are used in applications where the coating needs to withstand movement or impact without cracking.
- Sealants: Employed in sealing applications that require both flexibility and durability, such as in expansion joints in buildings.
10. UV-Curable Epoxy Resin
UV-curable epoxy resins are formulated to cure quickly upon exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light. These resins offer rapid processing times and are often used in applications where speed and precision are critical.
Properties:
- Rapid curing upon UV exposure
- High clarity and surface finish
- Good mechanical properties
Applications:
- Coatings: Used in fast-curing coatings for electronics, optics, and other high-precision applications.
- Adhesives: UV-curable adhesives are employed in industries requiring quick bonding times, such as in electronics assembly.
- 3D Printing: These resins are used in UV-based 3D printing technologies to create detailed and durable parts quickly.
Applications of Resin Epoxy
- Construction and Flooring
- Epoxy Flooring: One of the most popular uses of epoxy resin is in flooring, especially in commercial and industrial spaces. Epoxy floors are highly durable, resistant to chemicals and stains, and easy to clean, making them ideal for factories, warehouses, and garages.
- Concrete Repair and Coating: Epoxy resin is used to fill cracks and coat concrete surfaces, improving their durability and resistance to wear and tear.
- Automotive Industry
- Adhesives: Epoxy adhesives are used in the automotive industry to bond metals, plastics, and other materials. They provide strong, long-lasting bonds that withstand vibration and temperature fluctuations.
- Protective Coatings: Epoxy coatings are applied to car parts to protect them from corrosion and wear. These coatings are often used on engine parts, undercarriages, and other components exposed to harsh conditions.
- Marine Industry
- Boat Building and Repair: Resin epoxy is a popular material in the marine industry for building and repairing boats. Its waterproof properties and resistance to saltwater make it ideal for use in hull construction, sealing, and coating.
- Electronics
- Encapsulation and Potting: Epoxy resin is widely used in the electronics industry to encapsulate and protect delicate components from moisture, dust, and mechanical damage. It provides excellent insulation and protection for circuit boards and other electronic devices.
- Art and Crafts
- Jewellery Making: Artists and crafters use epoxy resin to create beautiful, custom jewellery pieces. The resin can be poured into moulds or used to encase small objects like flowers, stones, or glitter.
- Resin Art: Resin art has become a popular medium for creating unique, glossy paintings and sculptures. Artists mix epoxy resin with pigments and other materials to create abstract designs and three-dimensional works of art.
- Furniture and Home Décor
- River Tables: One of the most popular trends in furniture making is the epoxy river table. These tables feature a “river” of coloured or clear epoxy resin running through the centre, often incorporating wood or stones for added effect.
- Countertops: Resin epoxy is also used to create durable, custom countertops that mimic the look of natural stone or marble.
How to Use Resin Epoxy: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Preparation
- Tools and Materials: Before starting your project, gather all necessary tools and materials, including resin, hardener, mixing cups, stir sticks, gloves, and protective gear.
- Surface Preparation: Ensure the surface you are working on is clean, dry, and free of dust or debris. If working with porous surfaces like wood, consider sealing it with a primer to prevent bubbles.
- Mixing Resin Epoxy
- Measuring: Accurately measure the resin and hardener according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Incorrect ratios can lead to improper curing or a sticky finish.
- Mixing Technique: Stir the resin and hardener slowly and thoroughly to avoid introducing air bubbles. Make sure the mixture is well combined, with no streaks or unmixed areas.
- Applying Resin Epoxy
- Pouring: Pour the resin mixture onto your prepared surface. For large surfaces, pour in sections to ensure even coverage.
- Spreading: Use a brush or spatula to spread the resin evenly across the surface. Work quickly, as epoxy begins to cure within a specific timeframe.
- Curing Process
- Curing Time: Allow the resin epoxy to cure for the recommended time. This can range from a few hours to several days, depending on the type of resin and environmental conditions.
- Avoiding Dust and Debris: Cover your project with a dust cover or place it in a clean, dust-free area while it cures.
- Finishing and Polishing
- Sanding: Once the resin ep[oxy is fully cured, sand the surface with fine-grit sandpaper to remove any imperfections.
- Polishing: Apply a polishing compound to achieve a high-gloss finish. This step is optional but recommended for a professional-looking result.
5. Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
- Incorrect Mixing Ratios
- One of the most common mistakes is not measuring the resin and hardener correctly. Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions for precise measurements to ensure proper curing.
- Air Bubbles
- Air bubbles can form during mixing or application. To minimize bubbles, stir the mixture slowly and consider using a heat gun or torch to gently pass over the surface, which can help to release trapped air.
- Environmental Factors
- Temperature and humidity can affect the curing process. Work in a controlled environment where the temperature is consistent, and humidity levels are low.
- Poor Surface Preparation
- Failing to prepare the surface properly can lead to poor adhesion and a weak bond. Ensure surfaces are clean, dry, and properly sealed before applying resin epoxy.
- Overworking the Resin
- Overworking or constantly adjusting the resin after it’s been applied can lead to streaks, uneven surfaces, and other imperfections. Once the resin epoxy is poured and spread, let it settle and cure without further manipulation.
6. Health and Safety Considerations
- Safety Precautions
- Resin epoxy can be hazardous if not handled properly. Always wear gloves, safety glasses, and protective clothing when working with resin. Ensure your workspace is well-ventilated to avoid inhaling fumes.
- Handling and Storage
- Store resin and hardener in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight. Keep containers tightly sealed to prevent contamination and evaporation.
- First Aid Measures
- In case of skin contact, wash the affected area with soap and water immediately. If resin gets into your eyes, rinse thoroughly with water and seek medical attention.
- Disposal
- Dispose of unused resin and hardener according to local regulations. Never pour resin down the drain, as it can harden and cause blockages.
7. Environmental Impact of Resin Epoxy
- Sustainability Challenges
- While resin epoxy is a highly versatile material, it is not biodegradable. This poses environmental challenges, particularly in terms of waste disposal.
- Recycling and Disposal
- Some manufacturers are developing eco-friendly epoxy resins made from bio-based materials. Additionally, recycling cured resin products is possible, but it requires specialised facilities.
- Reducing Environmental Impact
- To minimise the environmental impact, use resin epoxy responsibly by recycling materials where possible and following proper disposal procedures.
8. Choosing the Best Resin Epoxy for Your Needs
- Factors to Consider
- When choosing a resin epoxy, consider factors such as the project type, desired finish, and environmental exposure. For example, UV-resistant epoxy is best for outdoor projects, while clear epoxy is ideal for decorative applications.
- Popular Brands
- Some of the top brands in the market include ArtResin, Pro Marine Supplies, and TotalBoat. Research customer reviews and product specifications to find the best option for your needs.
- Budget vs. Quality
- While budget-friendly options are available, investing in high-quality resin epoxy can result in better performance and longevity.
9. Trends and Innovations in Resin Epoxy
- Emerging Trends
- Resin epoxy is increasingly being used in creative industries, with artists and designers pushing the boundaries of what’s possible. From innovative furniture designs to interactive art installations, resin epoxy is finding new applications.
- Technological Advancements
- Advances in resin epoxy formulations are leading to faster curing times, improved UV resistance, and more sustainable options. These innovations are expanding the possibilities for both industrial and artistic uses.
Frequently Asked Questions
- How Long Does Resin Epoxy Last?
- The lifespan of resin epoxy depends on the environment and how well it’s maintained. Properly applied and cared for, epoxy resin can last for many years without losing its integrity.
- Can Resin Epoxy Be Used Outdoors?
- Yes, but it’s essential to use a UV-resistant epoxy to prevent yellowing and degradation when exposed to sunlight.
- Is Resin Epoxy Food Safe?
- Some epoxy resins are formulated to be food-safe once fully cured, making them suitable for use in countertops and food-contact surfaces. Always check the product specifications.
- What Should I Do If My Resin Doesn’t Cure?
- If your resin doesn’t cure properly, it could be due to incorrect mixing ratios, environmental factors, or expired products. Try to identify the cause and consider reapplying a fresh batch.
Corporate Office
Shadipur Metro Station, West Patel Nagar, New Delhi.
freshindiambi@gmail.com
Call
+91 7992295133
